National Bureau of Economic Research
Latest from the NBER
From the NBER Reporter: Research, program, and conference summaries
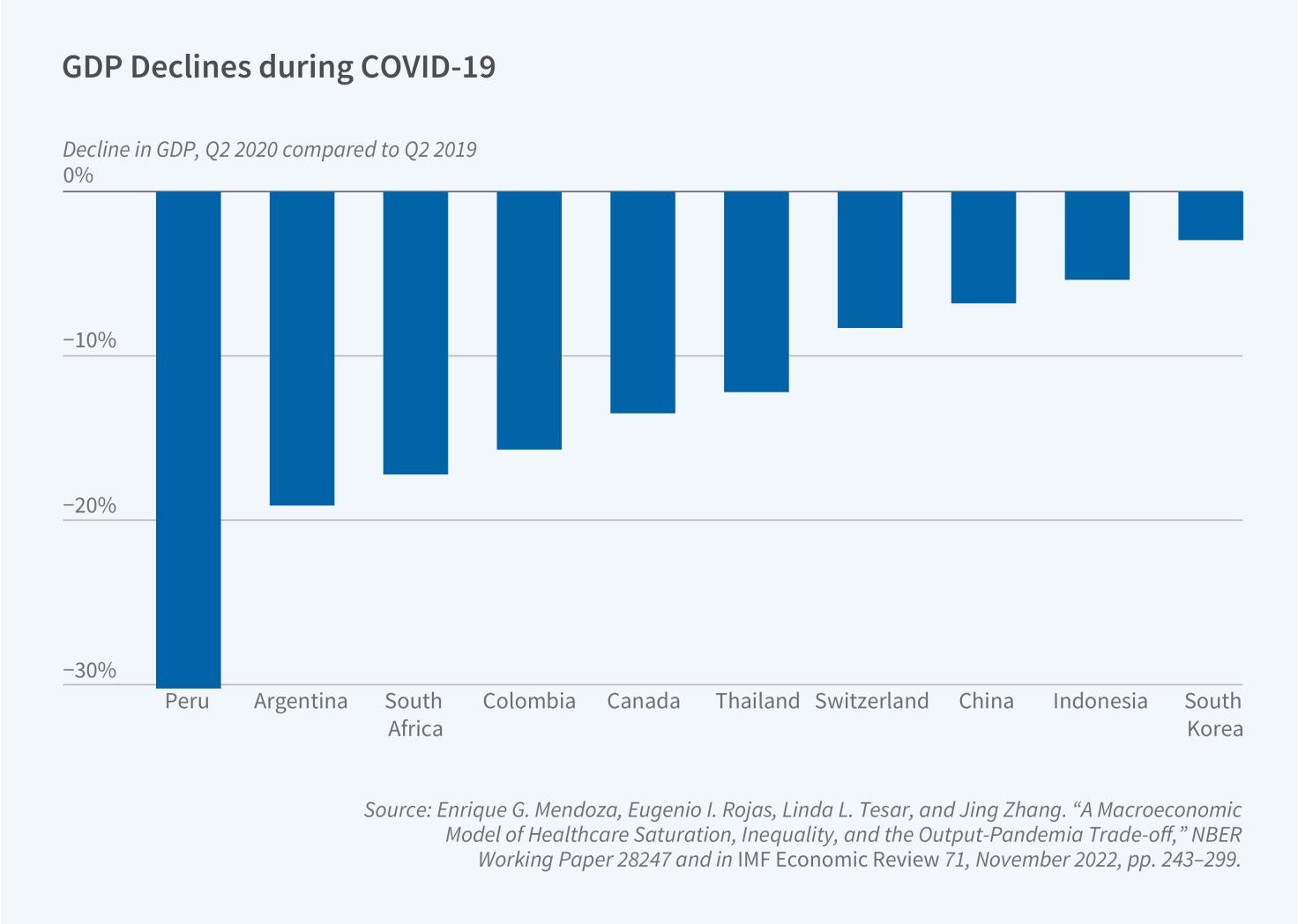
Program Report: International Finance and Macroeconomics
article
Affiliates of the International Finance and Macroeconomics (IFM) Program study financial interactions among nations, including cross-border capital flows, exchange rates, responses to global financial crises, and the transmission of economic shocks. Rather than attempting to summarize the more than 1,000 working papers these researchers have distributed since the last program report in 2015, we focus here on three issues that have attracted substantial research attention from this group: impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, global supply chain shocks, and the privileged position of the US dollar in global asset...
A research summary from the monthly NBER Digest
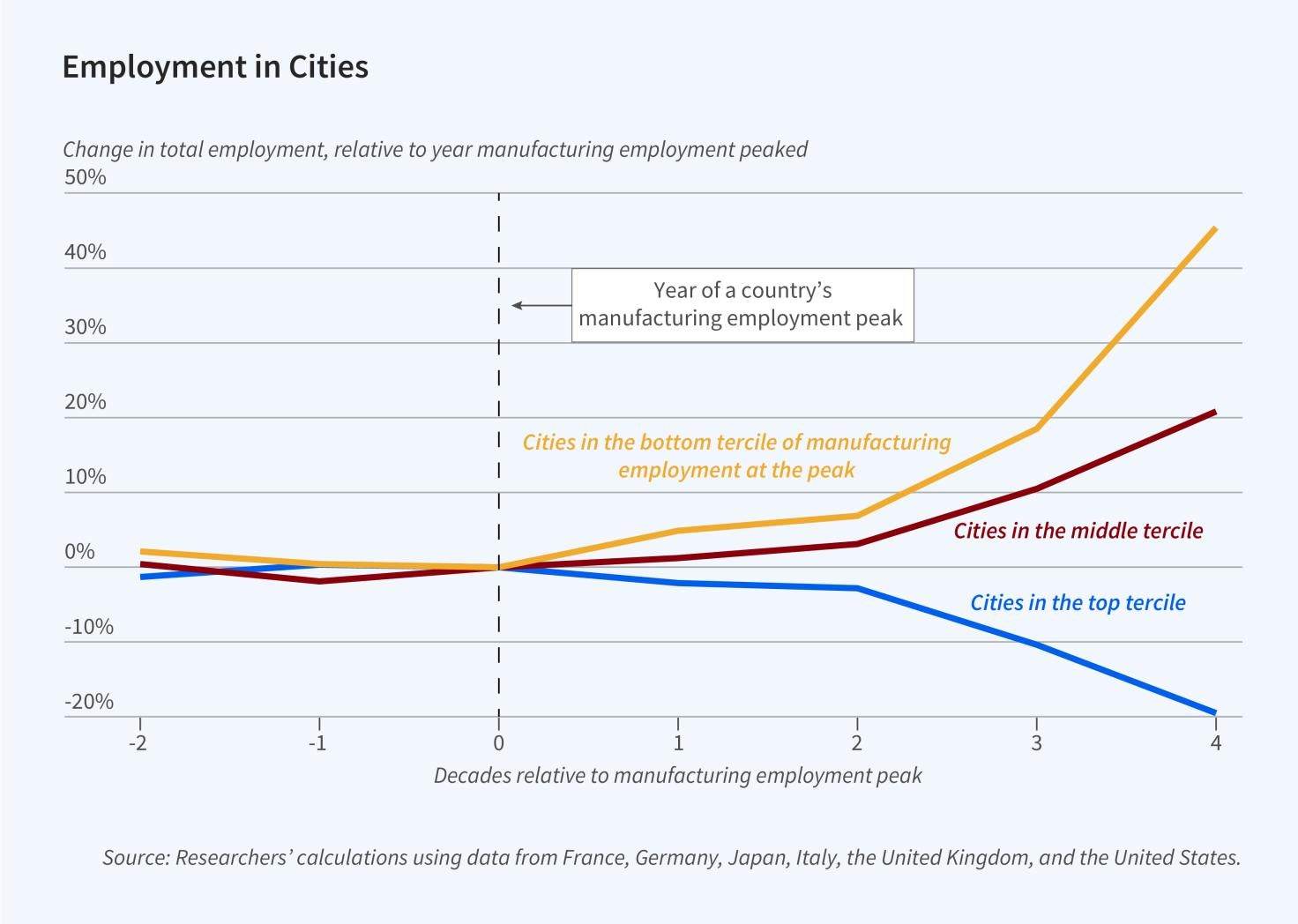
Global Evidence on the Decline and Recovery of Rust Belt Cities
article
Manufacturing employment peaked in the United States and the United Kingdom in the 1970s, in France and Italy in the ‘80s, and in Germany and Japan in the ‘90s. Each of these countries experienced deindustrialization that lowered manufacturing employment. On average, between the peak manufacturing year for each country and 2010, total employment rose by 7.5 percent while manufacturing employment dropped by 7 percent.
In The World’s Rust Belts: The Heterogeneous Effects of Deindustrialization on 1,993 Cities in Six Countries (NBER Working Paper 31948), Luisa Gagliardi, Enrico Moretti, and Michel Serafinelli find that cities with higher shares of college-educated workers were more likely to recover from the loss of manufacturing jobs, and that cities that depended more on manufacturing jobs...
From the NBER Bulletin on Health
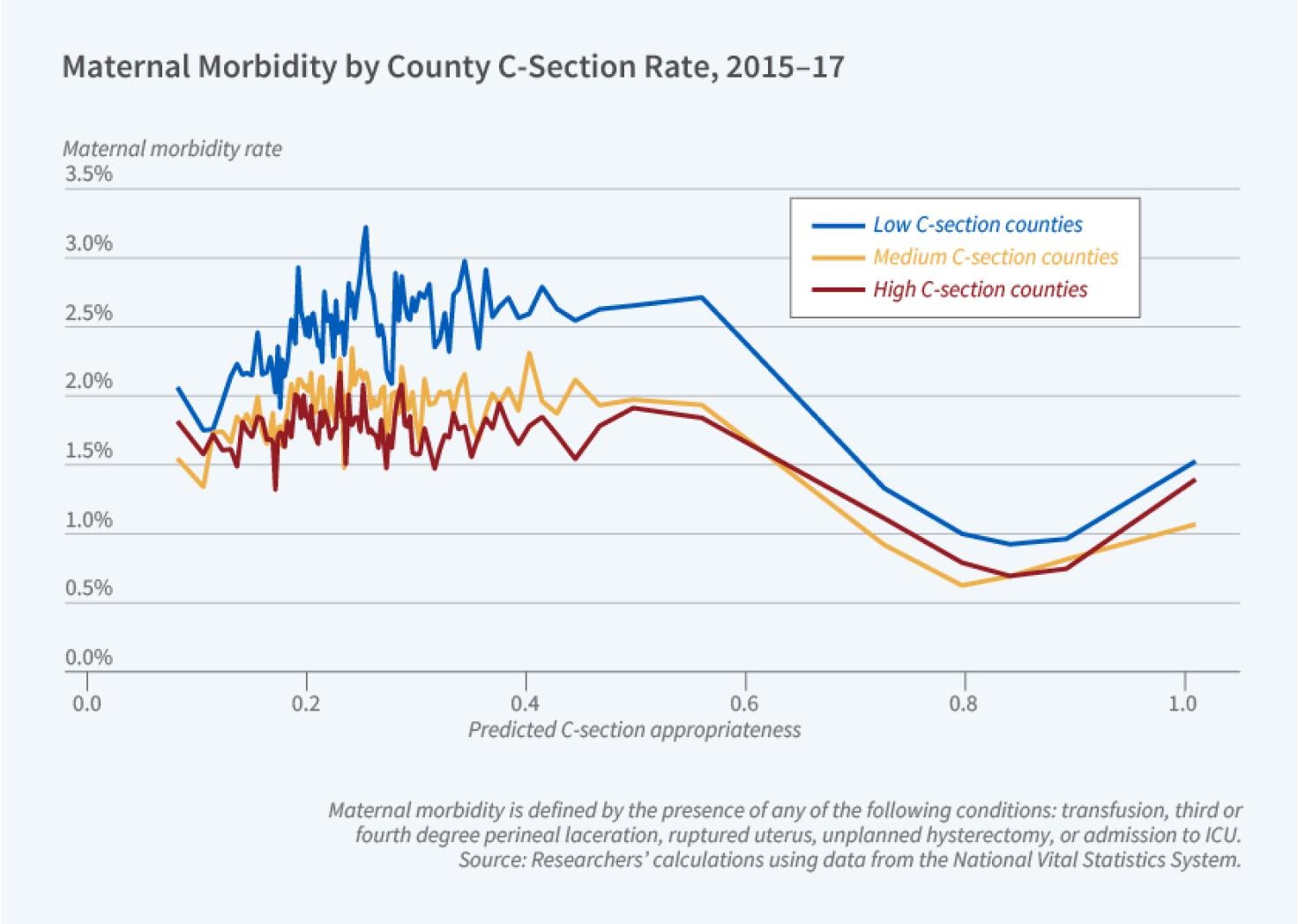
C-section Rates and Birth Outcomes
article
Cesarean section (C-section) is the most common surgical procedure performed in the United States. Sarah Robinson, Heather Royer, and David Silver report that C-section rates for first-time, singleton births increased from 24 percent to 32 percent between 1989 and 2017 alongside significant changes in medical practices during this period. In 2001, for example, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists began recommending C-sections for breech births. The rising rate of C-sections has sparked a debate about whether this procedure is being overused.
In Geographic Variation in Cesarean Sections in the United States: Trends, Correlates, and Other Interesting Facts (NBER Working Paper 31871), the researchers study how cross-county differences in C-section usage correlate with infant and maternal...
From the NBER Bulletin on Retirement and Disability
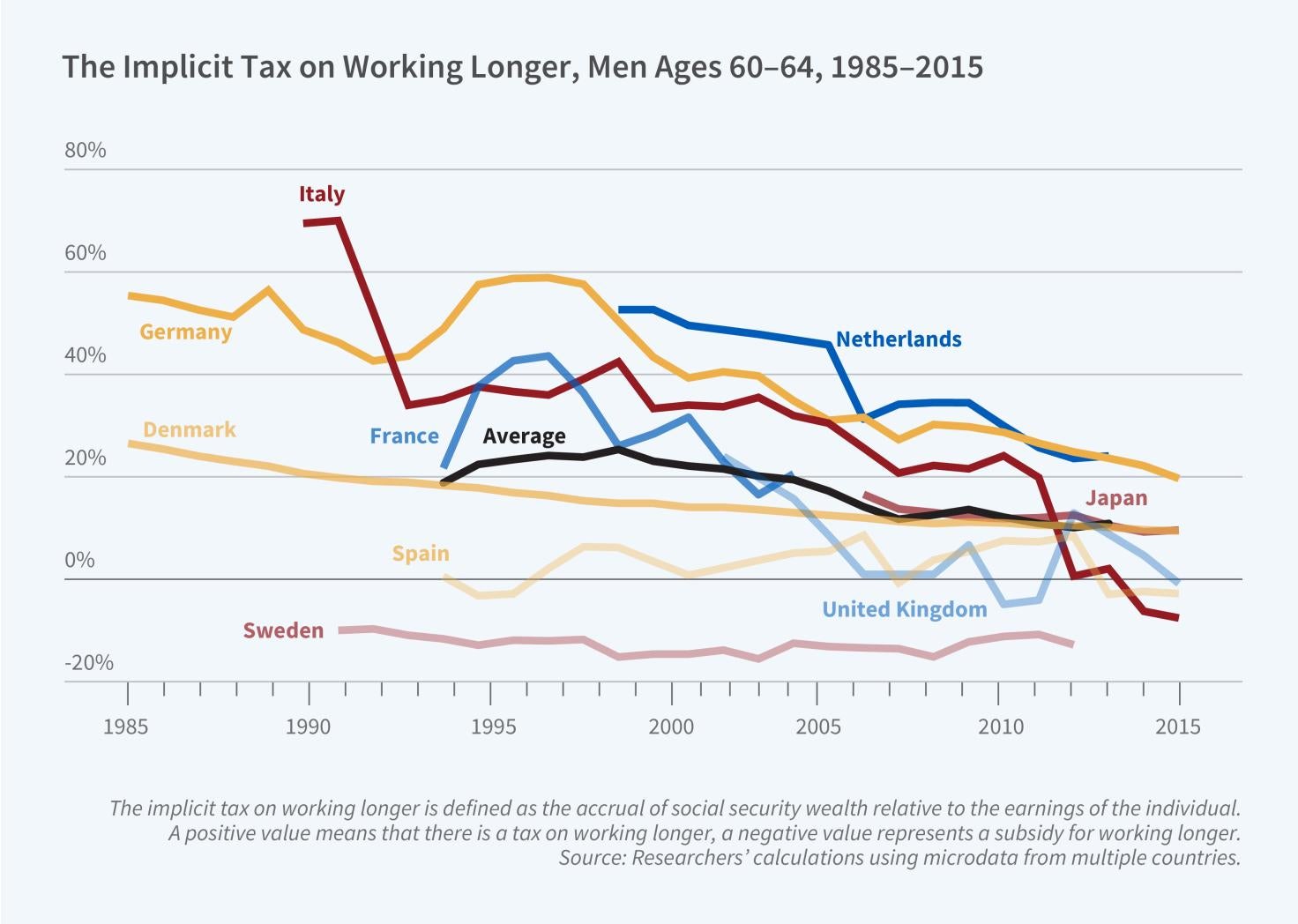
Social Security and Retirement around the World
article
Over the past 25 years, labor force participation at older ages has increased dramatically. In the 12 countries that are part of the NBER’s International Social Security (ISS) project, participation among those aged 60 to 64 has risen by an average of over 20 percentage points for men and over 25 percentage points for women.
In The Effects of Reforms on Retirement Behavior: Introduction and Summary (NBER Working Paper 31979), authors Axel Börsch-Supan and Courtney Coile report on the most recent work of the ISS project. The current analysis builds on previous project phases which showed that changes in health and education could…
From the NBER Bulletin on Entrepreneurship
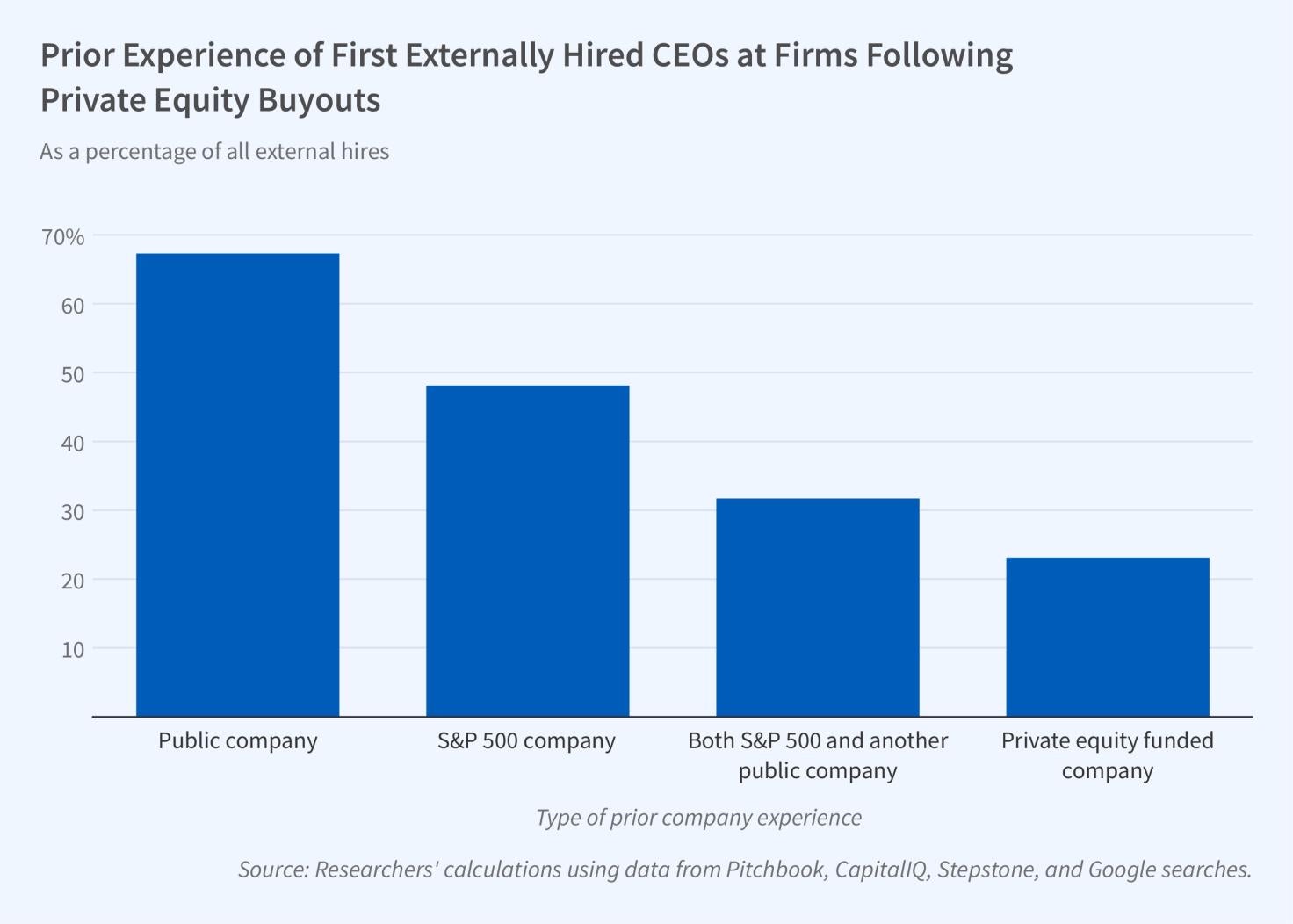
C-Suite Differences: Public versus Privately Held Firms
article
Private equity (PE) firms’ business model is to acquire privately held companies, to change their strategy and operations with the goal of improving profitability and growth, and ultimately to sell the companies for a profit. The senior management team is replaced at a majority of private equity acquisitions. More than 40 percent of PE firms report that this is a key way to improve their acquisitions’ success.
In The Market for CEOs: Evidence from Private Equity (NBER Working Paper 30899), Paul Gompers, Steven Kaplan, and Vladimir Mukharlyamov compare the characteristics of CEOs installed by PE firms to the characteristics of those who become...
Featured Working Papers
Analyzing experiences in seven advanced economies, Wenxin Du, Kristin Forbes, and Matthew N. Luzzetti find that central bank quantitative tightening announcements increase government bond yields and steepen the yield curve, but have limited effects on most other financial market indicators.
Research by Wei Lyu, George Wehby, and Robert Kaestner does not find any significant effects on infant health from federal stimulus checks and expanded the child tax credit during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A $1 increase in taxes on electronic nicotine delivery systems is associated with a 1-to-2 percentage point decline in teen marijuana use and a 0.8 percentage point reduction in adult marijuana use, Dhaval M. Dave, Yang Liang, Johanna Catherine Maclean, Caterina Muratori, and Joseph J. Sabia find.
Surveys of the US population by Stefanie Stantcheva indicate the predominant source of inflation aversion is a belief that it diminishes people’s buying power, thereby requiring costly adjustments in budgets and behaviors.
Capital regulation can reduce bank run risk by requiring capital raising, but its effectiveness depends on the regulatory capital definitions and can by eroded by the use of held-to-maturity accounting, according to João Granja, Erica Xuewei Jiang, Gregor Matvos, Tomasz Piskorski, and Amit Seru.
In the News
Recent citations of NBER research in the media
_______________________________________
Research Projects
Conferences
Books & Chapters
Through a partnership with the University of Chicago Press, the NBER publishes the proceedings of four annual conferences as well as other research studies associated with NBER-based research projects.
Research Spotlights
NBER researchers discuss their work on subjects of wide interest to economists, policymakers, and the general public. Recordings of more-detailed presentations, keynote addresses, and panel discussions at NBER conferences are available on the Lectures page.